FOCUS TECH
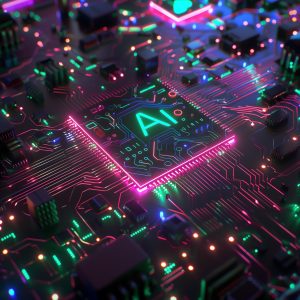
BRING YOUR OWN VULNERABLE KERNEL DRIVER (BYOVKD)
Facing the EDR behavioral supervision, attacker develops techniques for successful attacks by staying under the radars. One of these techniques is called BYOVKD: Bring Your Own Vulnerable Kernel Driver.
Even if it does not raise an alert on the EDR console, the Defense team must be vigilant to any telemetry that would indicate the loading of an unusual driver on assets. Furthermore, prevention mechanisms exist for this type of case, some examples below:
CERT-W: FROM THE FRONT LINE
THE FIRST RESPONDER WORD

READING OF THE MONTH
EMOTET
What is Emotet 2022?
Emotet is a Malware-as-a-Service (MaaS) relying on a botnet network which appeared in 2014. It was originally designed as a banking Trojan aiming to steal sensitive information related to bank accounts. In 2021, police forces arrested several people belonging to Emotet organization, which then reappeared with new features in 2022. The group behind Emotet seems to be opportunist and most of its victims are from US, UK, Japan, Germany, Italy, Spain, France, and Brazil.
Why is it dangerous?
Emotet is a polymorphic malware whose code changes over time. Among the numerous new features of the 2022 version, searchers from the DFIR Report have identified an ability to bypass anti-malware detection. To do that, Emotet 2022 uses a 64 bits base code and various signatures to avoid pattern recognition. The malware is also able to keep itself up to date once downloaded by using Command & Control servers, which send it updates the same as an Operating System. The MaaS is also able to release IcedID, which are modular banking Trojans able to drop other malwares. Doing so, Emotet helped to distribute ransomwares for impact, Cobalt Strike for initial access, XMRig for stealing wallet data…
How does Emotet 2022 initial infection work?
Using a phishing email with a malicious Office attachment, Emotet exploits a 2017 Microsoft vulnerability which allows remote code execution on vulnerable devices (CVE 2017-11882) to compromise its first victim.
Once downloaded in memory, the malware executes a sequence of legitimate Windows commands to perform a recognition of its environment, then spreads in the local network and steals information.
Emotet spreads through spam emails. According to Deep Instinct, 45% of them are containing malicious Office attachment such as Spreadsheets or scripts in most of the cases. As those emails traduce the object and attachments names in the target’s local language and come from known senders, the phishing looks particularly realistic.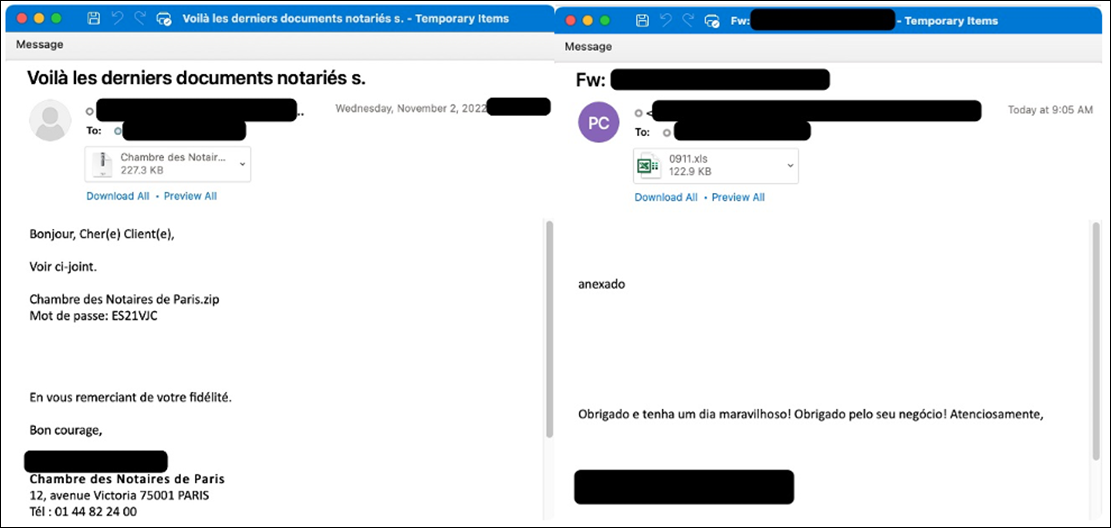
Comprehensive look of EMOTET fall 2022
Why is this new version of the MaaS particularly tricky?
Emotet 2022 can identify whether it’s downloaded into a sandbox environment, or a device connected to a network. In the first configuration it won’t activate itself, but in the second it will rely on a password dictionary to spread thanks to brute-force. Moreover, the November 2022 Excel files generally enclosed contains macros which no longer needs a user click to be authorized. The victim is only asked two things: copying the files into the Microsoft Office Template zone, which requires administrator privileges. Opening the file in this location will execute the macros without any warnings.
How to protect from Emotet 2022?
Since Emotet 2022 uses malicious spam and phishing is the most used technique for initial access, we highly advice you to consider these measures:
- Provide your company a solution against phishing.
- Launch an awareness campaign for employees and stakeholders.
- Provide you company an Endpoint Detection and Response which complete the anti-virus by performing behavioural analysis, which helps visualize the virus kill chain to identify the action levers.
Give a local administrator account to an employee only in case of specific need.
VULNERABILITY OF THE MONTH
DEBIAN-SPECIFIC REDIS SERVER LUA SANDBOX ESCAPE VULNERABILITY – CVE-2022-0543
Published by NVD: 18/02/2022
Products: Redis server for Debian and Debian-derived Linux distributions
Versions: less and equal to 5:5.0.14-1+deb10u2, 5:6.0.16-1+deb11u2, 5:7.0.5-1, 5:7.0.7-1
Score: 10 CRITICAL
Redis is an opensource NoSQL database management system. Redis includes an embedded Lua scripting engine, it allows client to run scripts. By design, the Lua engine must be sandboxed: it means that packages and APIs available are limited in an execution context. Redis clients are not allowed to execute arbitrary code on the Redis server.
In some Debian and Debian-derived Linux packages, the Lua environment is not sufficiently regulated because the Lua Library is provided as a dynamic library. It can allow attackers to access arbitrary Lua functionalities and results in a Lua Sandbox escape.
Early December, reports indicate that attackers are exploiting this vulnerability to deploy a new backdoor malware dubbed Redigo on Redis Server. The malware communicates with a server of command and control using port 6379 which is a legitimate port used by Redis for communication between client and server: the Redis server joins a botnet network.
According to Aqua, the malware has some functions specially written to the Redis server which may imply that the group behind this desired to build an adjusted attack that would target Redis servers.
A successful attack implies that attacker could execute arbitrary commands and access to sensitive information.
A group of attackers is behind the Redigo malware which is an emerging threat. Furthermore, the exploit of the CVE-2022-0543 is public and is used in the wild to deploy the malware. Vulnerable Redis Server must be patched and up to date.
SEE YOU NEXT MONTH!!